Robert Shaw MRTPI is a CPD trainer and town planner specialising in sustainability (Energy, climate change and sustainable housing)
 Renewable energy is increasingly featured in planning applications for local planning authorities (LPAs). Policies at all levels support the development of solar, wind, and battery storage, emphasizing their role in achieving carbon net zero, creating jobs, and supporting housing and economic growth.
Renewable energy is increasingly featured in planning applications for local planning authorities (LPAs). Policies at all levels support the development of solar, wind, and battery storage, emphasizing their role in achieving carbon net zero, creating jobs, and supporting housing and economic growth.
Renewable energy, along with technologies like electric vehicles, additive manufacturing, and artificial intelligence (AI), is growing exponentially and will have broad and transformative impacts on places, landscapes and the economy. While net zero is a commendable goal by itself, renewable energy will deliver much more and should be central to spatial and economic growth strategies.
Currently, when planners, elected members, and communities question the location of a proposal, applicants typically cite secured grid connections, willing landowners, and acceptable planning and environmental impacts. This situation reflects what technology author Azeem Azhar calls the "exponential gap" – the disconnect between rapid technological adoption and slower institutional responses, including spatial planning.
The National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF), published in December, encourages LPAs to identify suitable areas for renewable and low carbon energy sources and supporting infrastructure.
Three interrelated themes highlight the importance of spatial planning:
- Exponential Growth: The cost of renewables, especially solar and battery storage, has plummeted (Image 1), leading to larger and more numerous projects that have far exceed industry expectations globally (Image 2).
- Housing Ambitions: LPAs and property developers realise that housing goals are unattainable without secure and affordable grid connections.
- Economic Sectors: Growth in priority economic sectors, like AI-driven data centres, depends on access to low-cost power.
Image 1 – How the cost of renewables, especially solar and battery storage, has plummeted
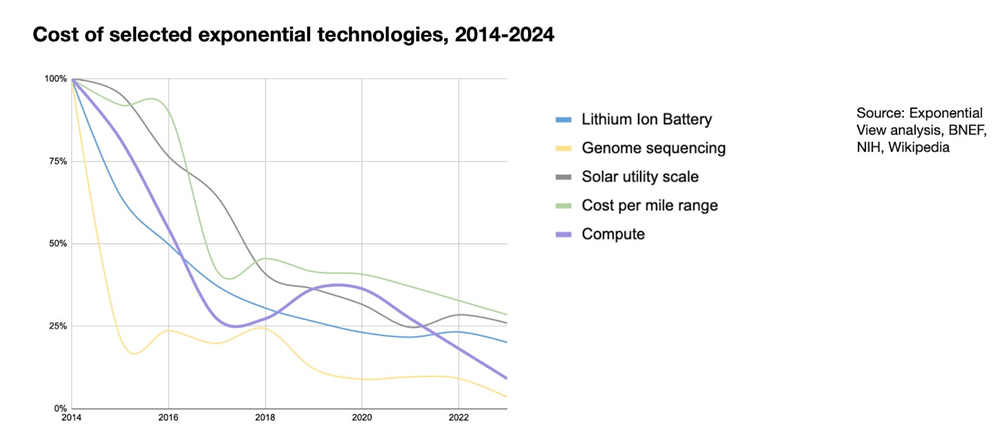
Sources: Exponential view analysis, BNEF, NIH, Wikipedia
Image 2, Cost reduction of renewables lead to larger and more numerous projects that have far exceed industry expectations globally

Strategic and local plan-making are crucial but not sufficient. Energy developers, and increasingly residential and commercial developers, will go where grid access is available. The newly formed National Energy System Operator is preparing a spatial plan for energy infrastructure.
It's imperative that new strategic and local plans engage with this to ensure renewable energy projects are optimally located, drive economic growth, and support positive spatial outcomes.
If you would like to know more about this topic join us for the next upcoming CPD webinar I will lead: Site allocation for renewable energy.
These sessions will help public sector planners:
- Recognise the importance of considering exponential change in renewable energy in plan-making.
- Identify suitable areas for renewable energy in the context of spatial, economic, and housing growth strategies.
- Collaborate to ensure these strategies are deliverable alongside grid expansion.


